-1.png?width=300&name=Factory%20floor%20machine%20data%20shown%20in%20real%20time%20(1)-1.png)
Kaizen in Manufacturing
Learn About the Fundamentals of Kaizen in Manufacturing
Kaizen refers to continuous improvement within a factory through small but regular changes. The method involves a philosophy of constant refinement in processes, encouraging ongoing efforts to enhance efficiency and quality while simultaneously reducing waste.
Read on to find out about the fundamentals of the Kaizen methodology, measuring the impact, tools and techniques to use, and most importantly, how you can start your continuous improvement journey.
What is Kaizen?
The Kaizen methodology is a technique used to implement small, incremental changes within a factory, which is also known as 'continuous improvement’.
Kaizen is a method of lean management, which was first introduced and used by Toyota in 1950.
To adopt a culture of continuous improvement, all employees (no matter their position or seniority) are encouraged to give feedback on current processes (large and small).
This taps into the skills and knowledge of every single staff member, empowering them to contribute their ideas, share knowledge, and actively participate in the improvement process.
Creating a culture that is always looking to improve requires ongoing training, regular audits/review meetings and management commitment to reinforce the importance of maintaining standards - this should be of utmost importance if you are to see results.
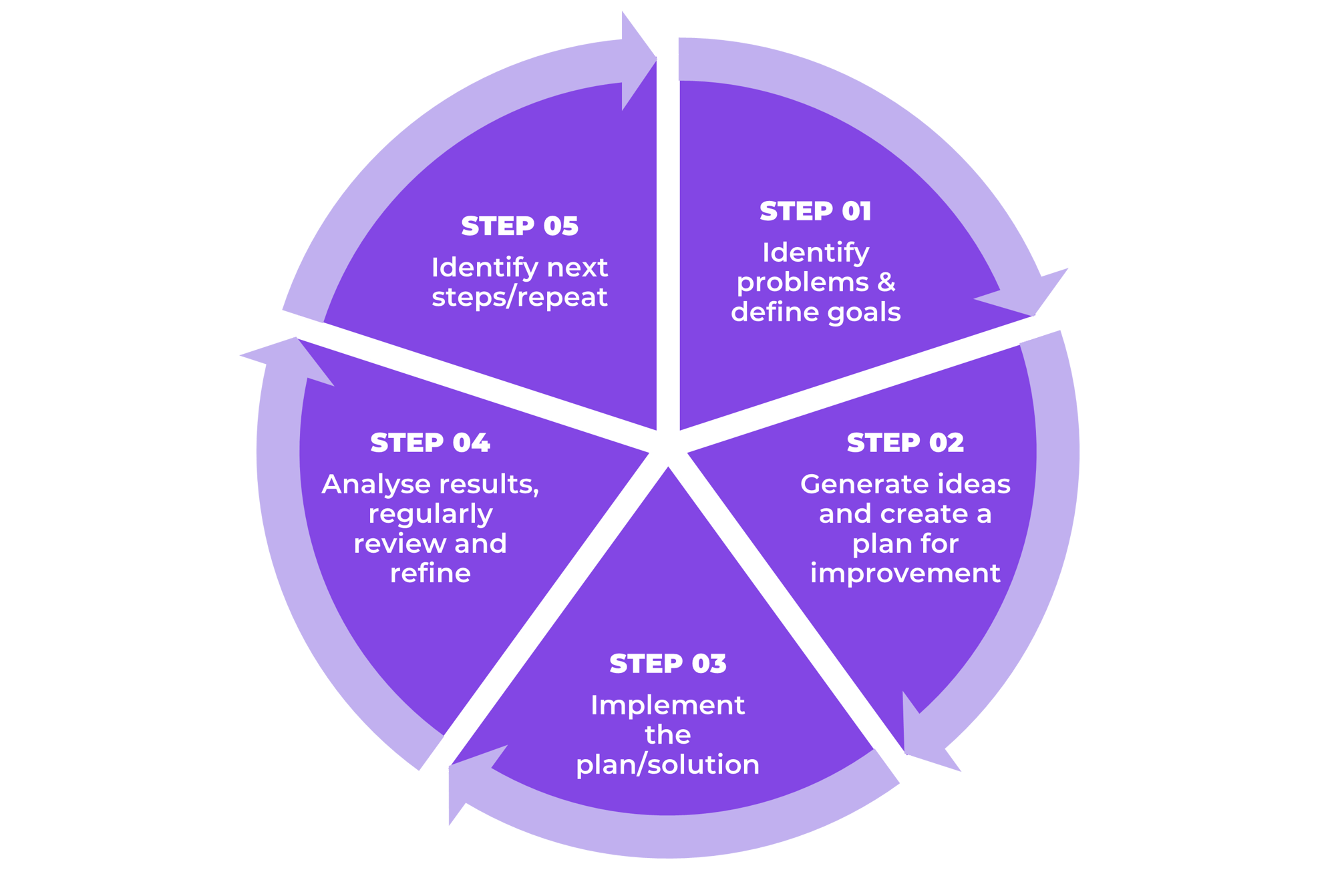
A Typical Kaizen Process
01. Identification:
Identify a specific area or process that requires improvement.
02. Generate Ideas and Create a Plan for Improvement:
Look for actionable ways to address the issues identified.
03. Implement the Plan/Solution:
Implement the chosen improvement solutions in a controlled and structured manner.
04. Analyse Results Regularly, Review, and Refine:
Measure the impact of the implemented changes, assess the results, and gather feedback for further improvements.
05. Identify Next Steps/Repeat:
Once successful improvements are identified, establish new standards, and develop processes to sustain the gains.
For a more detailed explanation of the five steps to implement kaizen in manufacturing, read our helpful blog.
Continuous Improvement Guide
Looking to implement a continuous improvement strategy to improve your factory's productivity? Download our FREE step-by-step guide.The Five Elements of Kaizen
01 Teamwork and Collaboration
Encouraging teamwork and collaboration is crucial for successful Kaizen implementation.
By involving employees from different departments and levels, organisations can tap into diverse perspectives, knowledge, and experiences. Teamwork fosters a sense of ownership, collective problem-solving, and shared responsibility for driving improvements.
02 Personal Discipline
Personal discipline plays a vital role in Kaizen. It involves an individual commitment to follow standardised procedures, maintain workplace cleanliness, and adhere to safety protocols. With personal discipline, employees can consistently contribute to a productive and efficient work environment.
03 Improved Morale
Kaizen initiatives can positively impact employee morale. When employees are actively engaged in the improvement process, they gain a sense of empowerment, as their ideas and suggestions are listened to and considered by peers. In turn, this boosts motivation, job satisfaction, and overall morale within the organisation.
04 Quality Circles
Quality circles are small groups of employees who come together regularly to identify, analyse, and solve problems related to quality and process improvements. These circles are platforms for sharing knowledge, brainstorming ideas, and implementing innovative solutions. Quality circles promote a culture of continuous learning and improvement within teams.
05 Suggestions for Improvement
Encouraging employees to provide suggestions for improvement is a fundamental aspect of Kaizen. Organisations should establish channels for employees to share their ideas, observations, and suggestions related to process enhancements.
This creates a culture that values employee input and fosters a mindset of continuous improvement.
By implementing the five elements of Kaizen, organisations can drive efficiency, improve quality, and foster a culture of innovation.
In doing so, manufacturers can put themselves in the best possible position to achieve sustainable long-term growth, retain and attract the best people and stay ahead of the competition.
Achieving a Kaizen 'Mindset' Culture
To achieve a Kaizen culture in manufacturing, organisations should consider the following factors:
Set Clear Goals:
Define clear goals and objectives for Kaizen initiatives, aligning them with the overall organisational strategy.
Provide Support and Resources:
Allocate adequate resources to support Kaizen’s efforts, including time, training, tools, and technology.
Embrace Risk-Taking:
Create an environment that encourages risk-taking and experimentation. Embrace failures as learning opportunities and encourage innovative thinking.
Continuous Evaluation:
Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of Kaizen initiatives, monitor progress, and make adjustments as necessary. Kaizen is an ongoing journey, requiring constant evaluation and refinement.

Maintaining a Kaizen Culture
If you want to maintain a culture of continuous improvement as employees come and go, it is important you have the following processes and mindset in place to enable Kaizen to thrive throughout the business:
Standardisation
Strong foundation maintained by implementing best practices, with new hires informed of and aligned with the company's core values for consistent processes.
Sustaining Discipline
Ongoing adherence to standardised processes, utilising regular audits and key performance indicator measurements for Kaizen-driven reviews.
Employee Empowerment
Creating a supportive atmosphere where employees freely share ideas, contribute knowledge, and actively engage in the entire Kaizen process.
.png?width=300&name=Production%20manager%20and%20operator%20looking%20at%20machine%20data%20(1).png)
Is Kaizen and 5S the Same?
While Kaizen and the 5S methodology are closely related and often implemented together, they are not the same concept.
5S is a workplace organisation methodology that originated in Japan. Today it is used in various industries worldwide. It functions to create a clean, organised, and efficient work environment by eliminating waste and promoting visual management. The term "5S" represents five Japanese words that describe the steps involved in implementing the methodology. The steps are often translated as:
- Sort: Sorting through all items in the workplace to determine what’s essential and disposing of anything that’s not required.
- Set in Order: Organising all items logically so everything is in a convenient and accessible place.
- Shine: Cleaning the workplace so that it’s tidy and free from dirt and hazards.
- Standardise: Establishing standardised procedures that improve efficiency and ensure consistency.
- Sustain: Sustaining and continuously improving on the progress achieved.
Kaizen focuses on continuous improvements, whereas the 5S methodology specifically addresses workplace organisation and cleanliness. Both approaches complement each other, with the 5S methodology providing a foundation for maintaining an organised and efficient workplace, which then serves as a platform for Kaizen initiatives.
The main differences between Kaizen and 5S relate to the strategy.
Kaizen and 5S both share the goal of improving processes, but utilise different strategies to arrive at this goal. Kaizen can constitute daily events that identify incremental improvements in operations across a business. Its purpose is to involve all employees and identify small improvements across the board, with the ultimate aim of enhancing productivity, quality, and customer satisfaction while also reducing waste.
5S is an organisational strategy that aims to create the optimal environment and procedures for efficient work. It involves sorting through materials so that nothing unnecessary interferes with work, ensuring workspaces are clean, safe, and organised, creating and standardising effective procedures, and more. Once this methodology is achieved, a 5S strategy functions and sustains and improves upon these results across the business.
Ultimately, the key difference between Kaizen and 5S is that the former seeks out novel ways to improve working processes. While the latter seeks to cultivate and sustain optimal environments and procedures that can be made consistent across the company.
How FourJaw Machine Monitoring Software Can Support Kaizen
You can’t continuously improve your factory without measuring the impact of your changes. With FourJaw's machine monitoring software, you can monitor key production and operational data such as machine downtime, OEE, and energy consumption, to name a few.
This can help you to:
- Identify bottlenecks in production
- Improve production line efficiency
- Reduce production costs
- Reduce machine downtime
- Plan resources more efficiently
Tracking these metrics over time allows teams to identify key areas for improvement and track their progress towards their goals.
Additionally, FourJaw's advanced reporting features provide a visual representation of data, making it easier for teams to interpret and communicate their findings to stakeholders and inform the continuous improvement and optimisation of processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes - without a doubt. In today’s climate, it is absolutely essential that manufacturers optimise their processes to reduce waste, cut costs, and improve employee morale in order to remain competitive, and most importantly, profitable.
With inflation in the UK hitting a peak of 11.1% in October of 2022, many businesses are seeing the cost of raw materials increase, so waste reduction (in all forms) has become of utmost importance. Kaizen is just one of the ways that you could work towards decreased production costs.
Kaizen isn’t a one-and-done task. It is something that should be ingrained in your company culture and practised day after day. However, if you are struggling to implement Kaizen, follow these simple steps:
- Identify problems & define your organisational goals
- Generate ideas & create a plan for improvement
- Implement your plan - actioning quick wins first
- Analyse the results regularly, reviewing and refining as needed
- Repeat the processes
Find out more in one of our helpful articles: How to implement a Continuous Improvement strategy
Kaizen utilises a range of tools and strategies to continually optimise processes across the business. You can use as many or as few as you like:
- Machine Monitoring Software (like FourJaw, for example)
- PDCA Cycle
- Value Stream Mapping
- Fishbone Diagrams
- Pareto Charts
Get started by booking a demo of FourJaw’s machine monitoring tool.
Not only can implementing a culture of continuous improvement help you to meet and exceed customer expectations but the Kaizen methodology can help you improve in several other areas:
- Waste Reduction: The 8 wastes of lean management are reduced through more efficient processes.
- Improved Output: Production processes are often sped up, with defects being brought to a minimum.
- Better Communication: Fosters a culture of teamwork, with different staff members working together towards a common goal.
- Employee Morale: Gives staff members a sense of value and belonging within the business.
- Costs Savings: Steps within production that don’t add value are reduced, saving time and decreasing overall production costs.
- Innovation & Competitiveness: Kaizen allows businesses to remain agile and adapt to the market’s current demands.
It is important to note that Kaizen isn’t always plain sailing; it can be hard to implement the idea into existing businesses, and a few ‘bad eggs’ could easily ruin the culture that you’ve worked so hard to build and maintain.
The word Kaizen is a combination of two Japanese words, which are “improvement” and “good change”. The “Kai” in Kaizen means “change” and “zen” means “good”. Today, these terms together mean “continuous improvement”.


